...
| Info |
|---|
Controlled Mend Integration Release This is a controlled Mend integration release. For more information, please contact support@whitesourcesoftware.com. |
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Introduction
| Info |
|---|
Supported Bitbucket Products This integration only supports Bitbucket Server and Bitbucket Data Center instances (this documentation applies to both services). It does not currently support Bitbucket Cloud instances. |
Mend for Bitbucket Server is a Bitbucket Server app, scanning your repositories, as part of your Mend account.
It is an integrated product within Bitbucket Server that shows a high-level security overview in the Bitbucket repository, detects all open source components and displays all vulnerabilities for these components.
It generates comprehensive up-to-date reports on the Bitbucket Server ‘Mend integration’ tab of the scanned repository. In addition, you will be able to view the scanned repositories in the Mend portal.
Mend for Bitbucket Server is part of Mend Developer Integrations and includes continuous automated dependency updates with Mend Remediate, using fix Pull Requests.
Prerequisites
The following requirements must be accommodated before installing the Mend server software.
Access to a working Mend Application and a user with Admin privileges (either Organization or Product Admin).
Bitbucket version 5.15 or above is installed.
Admin privileges on the Bitbucket instance
The deployment includes two environments:
Build environment where the image is built.
Deployment environment where the image is deployed.
Build Environment
This build environment can be the same one as the deployment environment on which the Mend Docker image is deployed. It requires the following:
Hardware Requirements
CPU: Dual-Core, 2Ghz or higher (Intel or AMD)
RAM: 16GB
Storage: 16 GB
Environment Requirements
An internet connection for the entire duration of the build procedure.
When using a Container Orchestration Platform (i.e Kubernetes, ECS, Rancher etc.), please make sure you have logs collection in place: ELK, Splunk or similar. If you are not using an Orchestration platform for the containers, the logs will be collected in designated folders.
A user with admin privileges: If the operating system is Windows, then you must have administrative privileges. If the operating system is Linux, then you must have root privileges.
Docker server version 18 and above. You can verify the Docker version by entering the following:
| Code Block |
|---|
docker –version |
Software and files delivered by Mend:
Mend Docker distribution artifacts that are delivered as a tar.gz or zip file (For example, agent-4-bitbucket-19.2.1.tar.gz or agent-4-bitbucket-19.2.1.zip).
You can obtain these files from Mend Support.
Target Environment
The image is installed on the target environment. This environment requires the following:
Hardware Requirements
CPU: Dual Core, 2Ghz or higher (Intel or AMD)
RAM: 16GB
Storage: 16 GB
Environment Requirements
A user with admin privileges: If the operating system is Windows, then you must have administrative privileges. If the operating system is Linux, then you must have root privileges.
Docker server version 18 and above. You can verify the Docker version by entering the following:
| Code Block |
|---|
docker –version |
Port 5678 must be open at all times. This port will be used to receive webhooks from the Bitbucket add-on.
Access to the Mend Application is required at times for the operation of the Mend for Bitbucket Server.
| Info |
|---|
The access to the app can be checked by issuing an HTTP GET request using a web browser or a utility (e.g., cURL, wget): It is recommended to verify that the returned status is 200 (OK). |
If a proxy server is available, then the following proxy settings need to be obtained:
URL
Port number
Username and password (for authenticated access)
A valid SSL certificate and KeyStore containing the certificate.
User Steps on Build Machine
Prepare for Installation
Download the ‘tar.gz’ file (‘agent-4-bitbucket-<version>.tar.gz’) for Linux or 'zip' file Windows (‘agent-4-bitbucket-<version>.zip’)
Installation and Configuration
In Windows, extract ‘agent-4-bitbucket-<version>.zip’ to an empty folder. In Linux, extract ‘agent-4-bitbucket-<version>.tar.gz’ to an empty folder.
The extraction creates the following items:
‘wss-bb-add-on’: Includes the jar of the add-on that will be uploaded to your Bitbucket server.
‘wss-bb-app’: Mend BitBucket server application. This application is responsible for communication between Mend application and Mend Bitbucket add-on. (located in the path 'wss-bb-app/docker/Dockerfile')
‘wss-config’: UI Configuration tool and related configuration file template.
'wss-deployment': Deployment template (for example, deploying the integration using Helm charts)
'wss-remediate': Mend Remediate worker
‘wss-scanner’: Mend BitBucket repository-scanner. wss-scanner is responsible for scanning Bitbucket repositories. (located in the path 'wss-scanner/docker/Dockerfile')
‘build.sh’/'build.bat’ (Linux/Windows): The build script
Modifying the Scanner Dockerfile
See here for more information on which package managers are part of the scanner image as well as how to add additional package managers.
Installing the Mend App in Bitbucket Server
There are two ways to install the Mend App in Bitbucket Server - by installing the app via the Atlassian marketplace for Bitbucket, or by uploading the JAR file directly from the extracted Mend for Bitbucket folder. For Bitbucket Data Center only the second option is available at the moment.
Installing via the Atlassian Marketplace
Navigate to the Administration page (<your/bitbucket-server/url>:<port>/admin) and then click Find new apps under the ADD-ONS menu.
In the search field, enter Mend and press Enter. The Mend App is displayed.
Click Install.
Uploading the Mend App JAR file
Navigate to the Administration page (<your/bitbucket-server/url>:<port>/admin) and then click Manage apps under the ADD-ONS menu.
Click Upload app and select the JAR file located in the wss-bb-add-on folder.
Click Upload.
Creating a Bitbucket Mend user and generating a Mend Activation Key
...
Navigate to the Users page under the ACCOUNTS menu (<your/bitbucket-server/url>:<port>/admin/users) and create a new user for Mend in your Bitbucket server with a permission level “Bitbucket User”.
...
Log in to your Bitbucket server with this Service user.
...
Login to the Mend Application.
...
The displayed fields are the following:
Bitbucket Server URL: Your Bitbucket server URL. For example: https://bitbucketdev.com.
Bitbucket Username: Your Bitbucket Service user’s username. Notice: it must be a username, please do not insert an email.
Bitbucket Personal Access Token: Your Bitbucket Service user’s personal access token with maximum privileges for this user. See also an explanation about retrieving a personal access token in Bitbucket documentation. (Link in Bitbucket server: <your/bitbucket-server/url>:<port>/plugins/servlet/access-tokens/manage)
Bitbucket Webhook URL: Enter the webhook URL in the following format: http://<docker-wss-bb-app-destinationURL>:5678/payload.
When clicking on ‘Get Activation Key’, your activation key will be generated. A new Service user will also be created for this integration inside the Mend Application with a WS prefix. NOTE: Do not remove this Service user.
Running the UI configuration tool from the ‘wss-configuration’ Directory
This editor enables you to configure the deployment file according to your specific configuration requirements.
...
Please copy the Activation key that was generated in Mend application and paste it to 'Activation Key' property in the editor.
...
After you have finished editing, export the filled in configuration file by clicking the ‘Export’ button and saving the JSON file with the name prop.json in a different location. This file will be used when running the application.
Details on Attributes of the Configuration file
...
Section
...
Label
...
Name
...
Type
...
Mandatory
...
Description
...
Sample Value
...
General
...
Activation Key
...
bolt.op.activation.key
...
String
...
yes
...
Your generated activation key in the Mend application
...
Proxy
...
HTTP Proxy Host
...
proxy.host
...
Host Address
...
no
...
HTTP proxy host. Leave blank to disable. Default value: Empty
...
Proxy
...
HTTP Proxy Host
...
proxy.port
...
Integer
...
no
...
HTTP proxy port. Leave blank to disable. Default value: Empty
...
Proxy
...
Proxy User
...
proxy.user
...
String
...
no
...
Proxy Username (if applicable)
...
user
...
Proxy
...
Proxy Password
...
proxy.password
...
String
...
no
...
Proxy Password (if applicable)
...
abc123
...
Advanced
...
Controller URL
...
controller.url
...
String
...
no
...
The ability to modify the App container URL in case its default name (wss-bb-app) was modified. Default value: http://wss-bb-app:5678
...
...
Issues
...
Should Create Issues
...
bolt4scm.create.issues
...
Boolean
...
no
...
The ability to globally enable/disable Issues creation across all of your organization's repositories. Default value: true
(NOTE: Supported from version 20.5.1.3 only)
...
Issues
...
Should Create Build Status
...
bolt4scm.create.check.runs
...
Boolean
...
no
...
The ability to globally enable/disable build statuses across all of your organization's repositories. Default value: true
(NOTE: Supported from version 20.5.1.3 only)
| Info |
|---|
You can export the JSON file at any time, even if you did not finish editing it in order to save your configurations and to enable assigning the configuration of a specific section to the appropriate professional in your organization (e.g., datasource section may be assigned to the DBA of your organization). |
...
Optional step: If you want to pull the images from another machine and run them as a container, push them to your Docker registry.
Building and Tagging the Docker Images
There are three different ways of building the Docker images.
| Info |
|---|
A total of 3 images will be built: wss-bb-app, wss-scanner, and wss-remediate. |
1. Using an Executable Script File (Recommended)
Run the build.bat or build.sh executable script file (Windows/Linux).
Both files are located in the root of the extracted agent-4-bitbucket-<version>.zip or agent-4-bitbucket-<version>.tar.gz files.
For Windows:
Run build.bat file which is located in the main folder where you extracted the agent-4-bitbucket zip file.
In order to ensure that the build succeeded, run the command docker images and check if wss-bb-app and wss-scanner and wss-remediate images were created.
For Linux:
Run build.sh file which is located in the main folder where you extracted the agent-4-bitbucket tar.gz file.
In order to ensure that the build succeeded, run the command docker images and check if wss-bb-app and wss-scanner and wss-remediate images were created.
2. Manually Build the Images
To run the steps of the build file manually, run the following commands directly:
NOTE: If you have already run the build file, skip these steps and continue to Target machine: Running the Containers step.
| Code Block |
|---|
docker build -t wss-bb-app:<version> wss-bb-app/docker
docker build -t wss-scanner:<version> wss-scanner/docker
docker build -t wss-remediate:<version> wss-remediate/docker
# For example:
docker build -t wss-bb-app:19.9.1.1 wss-bb-app/docker
docker build -t wss-scanner:19.9.1.1 wss-scanner/docker
docker build -t wss-remediate:19.8.1 wss-remediate/docker |
NOTE: From version 21.5.1, the Remediate Dockerfile supports both Ubuntu 18.04 and Ubuntu 20.04-compatible images. The base image can be changed using the BASE_IMAGE build argument. e.g.
| Code Block |
|---|
docker build --build-arg BASE_IMAGE=ubuntu:18.04 -t wss-remediate:21.5.1 wss-remediate/docker |
3. Using a Docker Registry
If you are using a private Docker Registry, run the following commands to push the images into your registry:
| Code Block |
|---|
docker push <registry>/wss-bb-app:<version>
docker push <registry>/wss-scanner:<version>
docker push <registry>/wss-remediate:<version>
# For example:
docker push my-registry/wss-bb-app:19.9.1.1
docker push my-registry/wss-scanner:19.9.1.1
docker push my-registry/wss-remediate:19.8.1 |
After executing the commands, you should be able to view the images in your registry.
Target Machine: Run the Containers
Deploying Using Docker
On the target environment, create a directory (e.g., ‘<path/to/config/dir>’) and add to it the configuration properties JSON file (prop.json) that you previously edited and exported using the Configuration Editor.
Then, you will need to create a network bridge and run the following Docker containers by using Docker or Kubernetes.
Create a network bridge (this will create a private network between the different containers, since all containers need to run within the same network):
| Code Block |
|---|
docker network create -d bridge my_bridge |
...
| Code Block |
|---|
docker run --name remediate-server --network my_bridge -e LOG_LEVEL=debug -p 8080:8080 -v <path/to/config/directory>/prop.json:/etc/usr/local/whitesource/conf/prop.json -v /tmp:/tmp wss-remediate:<version>
# For example:
docker run --name remediate-server --network my_bridge -e LOG_LEVEL=debug -p 8080:8080 -v c:/tmp/bb/prop.json:/etc/usr/local/whitesource/conf/prop.json -v /tmp:/tmp wss-remediate:19.5.1 |
| Info |
|---|
Changing Remediate Server PortIf port 8080 is not available, you can use a different port by modifying only the second port in the 'docker run' command. For example: docker run --name remediate-server --network my_bridge -e LOG_LEVEL=debug -p 8082:8080 -v c:/tmp/bb/prop.json:/etc/usr/local/whitesource/conf/prop.json -v /tmp:/tmp wss-remediate:19.5.1 |
Run the 'wss-bb-app' app container:
| Code Block |
|---|
docker run --name wss-bb-app --network my_bridge -p 9494:9494 -p 5678:5678 -v <path/to/config/directory>:/etc/usr/local/whitesource/conf wss-bb-app:<version>
# For example:
docker run --name wss-bb-app --network my_bridge -p 9494:9494 -p 5678:5678 -v c:/tmp/bb/:/etc/usr/local/whitesource/conf/ wss-bb-app:19.5.1.1 |
Run the ‘wss-scanner’ scanner container:
| Code Block |
|---|
docker run --name wss-scanner-bb --restart=always --network my_bridge -p 9393:9393 -v <path/to/config/directory>:/etc/usr/local/whitesource/conf/ wss-scanner:<version>
# For example:
docker run --name wss-scanner-bb --restart=always --network my_bridge -p 9393:9393 -v c:/tmp/bb/:/etc/usr/local/whitesource/conf/ wss-scanner:19.5.1.1 |
Deploying Using Helm Charts
The wss-deployment folder consists of the following structure:
helm
configs
templates
config.yaml
wssScmIntegration.yaml
Chart.yaml
values.yaml
Copy the helm folder from wss-deployment to your target environment. Inside the helm/configs folder, add the configuration properties JSON file (prop.json) that you previously edited and exported using the Configuration Editor.
Chart.yaml
This file contains information about the chart.
NOTE: Do not edit this file.
Values.yaml
This file represents the Mend integration image names and versions.
| Code Block |
|---|
wsscanner:
image: {image}
version: {version}
wsscontroller:
image: {image}
version: {version}
wssremediate:
image: {image}
version: {version} |
For each image declaration (wssscanner, wsscontroller, wssremediate), replace {image} and {version} with the actual built image name and version. NOTE: For wsscontroller, use the name and version of the wss-bb-app image.
An optional parameter, imagePullSecrets, can be added to this file in case Docker repository authentication is required.
configs/prop.json
In the helm folder, create a new folder named configs, and add to it the configuration properties JSON file (prop.json) that you previously edited and exported using the Configuration Editor.
templates/config.yaml
This is a configuration file pointing to the configs/prop.json file.
NOTE: Do not edit this file.
templates/wssScmIntegration.yaml
This is a configuration file containing all the parameters for deploying the integration.
NOTE: In this file, there are 3 dashes ("- - - ") that separate the services Do not remove them.
In order for the webhook URL to be accessible publicly by the integration, a load balancer service must be added to the file. An example of such a service is provided below:
| Code Block |
|---|
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: lb1
namespace: acme
annotations:
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname: helm.acme.io
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-backend-protocol: http
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-ssl-ports: "443"
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-ssl-negotiation-policy: "ELBSecurityPolicy-TLS-1-2-2017-01"
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-ssl-cert: arn:aws:acm:us-east-7:834027593108:certificate/4720e07a-a231-4fd5-9c4a-12ab1450567d
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- port: 443
name: https
targetPort: 5678
selector:
app: wss-controller |
Activating the Mend Integration
| Info |
|---|
If the wss-bb-app webhook URL changes, then you will need to re-validate the activation key by performing step 2 again. |
Go to the Bitbucket server UI > Administration page > Mend Integration tab (Link:<your/bitbucket-server/url>:<port>/plugins/servlet/whitesource/configure).
Copy the activation key and paste it into the Activation key field, and then click Validate.
If you are integrating multiple repositories and want to apply global configurations, refer here before continuing in this procedure.
Select one of the following options:
All projects: (default) Integrate all the (current and future) projects inside the Bitbucket instance.
Selected projects only: Select specific projects that you would like to integrate with Mend.
The project admin must do the following:
Go to the project page of any integrated project (see above).
Go to the Project settings page.
In the navigation pane, under Workflow, click Mend Integration.
Select one of the following options:
All repositories: (default) Integrate all the (current and future) repositories inside the Bitbucket instance.
Selected repositories only: Select specific repositories that you would like to integrate with Mend.
NOTE: Only a user with Admin or Write permissions on a selected repository will be able to access the Mend Integration tab inside the repository page.
Click Save. Unless specified otherwise via the global configuration, an onboarding pull request is created for the selected repositories. This request contains a Mend configuration file (.whitesource) that can be customized before merging the pull request. The initial PR must be merged to the base branch first. This will then initiate the installation and start the first scan. You can then define further settings (like selected branches) in the .whitesource file.
Remediation
Mend Remediate provides continuous automated dependency updates, saving time and reducing your security risks. To read more and configure automated Pull Requests, see Mend Remediate.
Initiating a Scan
A Mend scan is initiated via a valid Bitbucket push command. A valid push command meets at least one of the following requirements:
One of the commits in the push command added/removed a source file(s) that has an extension supported by Mend.
Refer to the Mend Languages page in order to find out whether or not a specific language and its extensions are supported.One of the commits in the push command includes an addition/modification of the package manager dependency file(s).
Refer to the list of supported dependency files to find out whether your dependency files are supported.
NOTE: a push command may consist of multiple commits.
Inventory post-scan
Mend continuously researches new vulnerabilities and updates its vulnerability database with these findings. In order that these newly-discovered vulnerabilities be reflected in projects a soon as possible, Mend initiates a post-scan process for all integrated projects at 01:00 UTC and opens new issues for vulnerabilities that were added to the database in the previous 24 hours.
This is an automated procedure, and no action from the user is required.
Viewing Details of the Scan
Results can be viewed in the following places:
The Mend Integration tab within the project
The Mend Security/License Check within the Bitbucket repo Commits tab.
The Mend UI.
Via email notifications.
Viewing Details of an Issue
See here for more information.
Viewing Mend Security Checks
In the Commits tab you can view the status and results of each scan. Click a specific build icon in order to view the Builds page.
Types of Indicators
The following build status indicators are available as feedback on the head commits:
In progress: The Mend scan is in progress.
Success: The Mend scan completed successfully and no vulnerabilities were detected.
Failed: The Mend scan did not complete successfully, this is the default for all completed scans. NOTE: a failed status may be shown due to security vulnerabilities, or due to an error that occurred during the scan.
Samples of Status Check Indicators
In Progress
The following is a sample of a In Progress status, which indicates that the security check is currently scanning the head commit.
...
Success
When no vulnerabilities are found and no errors occurred during the scan, Mend will display the following status check, and a security report indicating that no vulnerabilities were detected:
...
Failed
...
Click on the ‘Mend Security Check’ link to view the security report on all vulnerabilities that were found for the specific commit’s scan. It includes the following columns:
...
CVE: A link to the related CVE page for the vulnerability. Displayed in a collapsible format (click the arrow to expand/collapse for more information regarding the vulnerability).
...
Severity: Overall score of the severity (High, Medium or Low).
...
Vulnerable Library
...
Suggested Fix
...
Issue - A link to the relevant issue generated by Mend (when available)
...
Scan failed: Due to system error or not a valid Bitbucket ‘push’ command.
Viewing Mend License Checks
In the Commits tab you can view the status and results of each scan. Click a specific build icon in order to view the Builds page.
Types of Indicators
The following build status indicators are available as feedback on the head commits:
Success: No license policy violations were detected.
Failed: One or more license policy violations were detected during the Mend scan.
Viewing Details in the Mend UI
Mend projects will have the same name as the corresponding Bitbucket repository, with a "BB_" prefix, unless otherwise specified in the .whitesource file using a project token.
The name of the Mend product will be the same as that of the Bitbucket project preceded by a "BB_" prefix if the Bitbucket repository is under a Project. Otherwise, the name will be your Bitbucket username preceded by "BB_".
Accessing Scan Statistics via API
See here for more information.
Health Check APIs
See here for more information.
The .Mend File
A WhiteSource configuration file (.whitesource) is a JSON file added to each repository that is enabled for a scan. It provides configurable parameters for the Mend scan.
The .whitesource file is only added in the default branch of the repository (unless modified, it is the master branch).
.whitesource file
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
{
"scanSettings": {
"configMode": "AUTO",
"configExternalURL": "",
"projectToken": "",
"baseBranches": []
},
"buildSettings": {
"displayMode": "diff",
"failBuilds": true
},
"issueSettings": {
"minSeverityLevel": "LOW"
}
} |
Parameters
Global Settings
...
Parameter
...
Type
...
Description
...
Required
...
Default
...
settingsInheritedFrom
...
String
When the global configuration is enabled, this parameter will specify the location of the whitesource-config repository from which it will inherit its configuration. It must contain the Bitbucket user name, repository name and branch (optional) of the repo-config.json file location. The default branch is 'master', but can be modified according to the location of the repo-config.json file in the whitesource-config repo.
NOTE: You can override specific parameters that are relevant only in the specific repository by adding these after this parameter.
Examples:
Using only values defined in the global configuration:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
"settingsInheritedFrom": "whitesource-config/whitesource-config@master" |
Using values defined in the global configuration and overriding the scan settings parameters:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
"settingsInheritedFrom": "whitesource-config/whitesource-config@master",
"scanSettings": {
"projectToken": "12345",
"baseBranches": ["master","integration"]
} |
...
No
...
N/A
...
overrideConfigAllowList
...
Array
...
When the global configuration is enabled, this parameter will regulate the ability of repositories that inherit their configuration from the whitesource-config repository to override the parameters locally. There are three options:
null (
"overrideConfigAllowList": null) - All repositories that inherit configuration from this .whitesource file can override them locally.Empty array (
"overrideConfigAllowList": []) - All repositories that inherit configuration from this .whitesource file cannot override them locally.Array with values (
"overrideConfigAllowList": ["orgName1/repoName1", "orgName2/repoName2"]) - Only specified in the array repositories that inherit configuration from this .whitesource file can override them locally.
NOTE: This parameter must be used in the repo-config.json file of the whitesource-config repository.
...
No
...
null
Scan Settings (scanSettings)
...
Parameter
...
Type
...
Description
...
Required
...
Default
...
configMode
...
String
...
The configuration mode to be used for each scan. There are three options:
AUTO - Automatic mode. This will use the default Mend configuration.
LOCAL - Local mode. This will look for a local 'whitesource.config' file to be provided in the root folder of the current repository. The configuration file should be in the same format as the Unified Agent configuration file. NOTE: Not supported in the Global Configuration.
EXTERNAL - External mode. This will look for a configuration file specified according to the configExternalURL parameter.
...
No
...
Auto
...
configExternalURL
...
String
The URL of the external configuration file (you can choose any filename). The configuration file content should be in the same format as the Unified Agent configuration file.
The following protocols are supported: 'ftp://', 'http://', 'https://'.
...
No
...
Empty
...
projectToken
...
String
Adds the ability to map a Bitbucket repository to a Mend project. The parameter used needs to be the Mend project token.
...
No
...
Empty
...
baseBranches
...
Array
...
Adds the ability to specify one or more base branches for which scanning results will be sent to a new Mend project.
Example usage: ["master", “integration"]
This will set both master and integration branches as base branches.
Note the following:
An Issue will only be created for the specified branch names.
For each specified branch, a Mend project will be created. The name of the project will contain a suffix "_branchname". For example, MyApp_dev. This suffix will not apply to the default branch.
NOTE: This parameter is available only from version 20.7.1.
...
No
...
Empty
In this case, the base branch only consists of the default branch.
...
enableLicenseViolations
...
Boolean
...
When enabled, a new Mend License Check will be generated for each valid push.
NOTES:
This parameter is available only from version 20.11.2.
You must have it least one policy of match type By License Group defined with a Reject action in the Mend UI.
The policy name in the Mend UI must start with a "[License] " prefix.
For example, "[License] PolicyName".
...
No
...
false
Build Settings (buildSettings)
...
Parameter
...
Type
...
Description
...
Required
...
Default
...
displayMode
...
String
...
How to display Mend security information for a scan performed on a non-base branch:
When set to diff - Only the diff of detected vulnerabilities between the current commit and its base branch commit will be displayed. NOTE: This value is only supported when using the baseBranches configuration.
When set to baseline - A summary of all detected vulnerabilities in the full repository inventory will be displayed.
...
No
...
diff
...
createBuildStatus
...
Boolean
...
The app can provide checks in commits and pull requests on any repository branch. This parameter defines whether Mend Security Check is going to run. If set to false it will not be initiated.
...
No
...
true
...
failBuilds
...
Boolean
...
The app provides checks in commits and pull requests on any repository branch. This parameter defines the conclusion status for when a Mend Security Check is completed.
When the parameter is set to false, the conclusion status of a Mend Security Check will always be 'Success', even if the check fails. This way, any repository member is able to merge a pull request, even if a Mend Security Check found security vulnerabilities.
When the parameter is set to true (default), the conclusion status of a Mend Security Check will be 'Failure' in cases where Mend Security Check found security vulnerabilities or an error occurred during the scan. When this configuration is defined, a policy for approving a pull request is enforced. In this setting, only the administrator of the repository can approve the merging of a pull request that contains one or more checks with a 'Failure' status.
...
No
...
true
...
failLicenseBuilds
...
Boolean
...
The app provides checks in commits and pull requests on any repository branch. This parameter defines the conclusion status for when a Mend License Check is completed.
When the parameter is set to false, the conclusion status of a Mend License Check will always be 'Success', even if the check fails. This way, any repository member is able to merge a pull request, even if a Mend License Check found license policy violations.
When the parameter is set to true (default), the conclusion status of a Mend License Check will be 'Failure' in cases where Mend License Check found license policy violations or an error occurred during the scan. When this configuration is defined, a policy for approving a pull request is enforced. In this setting, only the administrator of the repository can approve the merging of a pull request that contains one or more checks with a 'Failure' status.
...
No
...
true
...
showWsInfo
...
Boolean
Whether to show additional Mend information such as the project token inside the Mend Build Status (after the scan token).
Mend information is only displayed if the commit originated from a base branch.
If the commit exists in multiple branches, the Mend information displayed will only represent the origin base branch (i.e. where the baseBranches parameter was defined).
The following hidden JSON object will also be added inside the Build Status when this parameter is enabled:
| Code Block |
|---|
<!-- <INFO>{"projectToken":"8cd2d2a8651145c087609e0a43f783e95f7008cb908541498348fed529572e01"}</INFO> --> |
NOTE: Additional Mend data may be added inside the JSON object in the future.
...
No
...
false
...
useMendBuildNames
...
Boolean
...
If set to true names of all Checks (Security, License, SAST, IaC) will be named after Mend (e.g. “Mend Security Check”). If set to false all Checks will have word “WhiteSource” instead of “Mend”.
Note: When .whitesource is created the value of useMendCheckNames is true.
...
No
...
false
Issue Settings (issueSettings)
...
Parameter
...
Type
...
Description
...
Required
...
Default
...
minSeverityLevel
...
String
...
Enables users to decide whether to open a new Issue only if a certain severity level is available on a detected vulnerability.
Available values for minSeverityLevel:
NONE - No Issues will be generated.
LOW - Any Low/Medium/High vulnerabilities found will generate an Issue.
MEDIUM - Any Medium/High vulnerabilities found will generate an Issue.
HIGH - Any High vulnerabilities found will generate an Issue.
NOTE: The Mend Security Check summary is also affected by this parameter.
...
No
...
LOW
...
displayLicenseViolations
...
Boolean
...
Whether to generate an Issue for every detected license policy violation.
NOTE: This parameter is relevant only if enableLicenseViolations (scanSettings) is set to true.
...
No
...
true
(only if enableLicenseViolations (scanSettings) is set to true)
Remediate Settings (remediateSettings)
...
Parameter
...
Type
...
Description
...
Required
...
Default
...
enableRenovate
...
Boolean
...
When enabled, Remediate will raise automated Pull Requests for outdated dependencies in addition to Pull Requests remediating vulnerable dependencies. Remediate will then perform all the functionality and support all the configuration options available in Mend Renovate.
See Renovate configuration options for all configuration options.
Refer here for parameter usage.
...
No
...
false
...
transitiveRemediation
...
Boolean
...
Whether to enable transitive remediation for NPM repos.
When npm v6 (npm v7 is not currently supported) is used with a package-lock.json file, and vulnerabilities are found within transitive dependencies in the file, then in most cases Remediate is able to successfully remediate the vulnerability. Sometimes it may not be possible to successfully remediate because a parent dependency does not yet have a new release that allows the necessary fixed-in version of the transitive dependency.
...
No
...
false
...
workflowRules
...
Object
This parameter is used to specify the rules that regulate when to open remediation pull requests.
Usage examples:
| Code Block |
|---|
"remediateSettings": {
"workflowRules": {
"enabled": true,
"minVulnerabilitySeverity": "LOW"
}
}
"remediateSettings": {
"workflowRules": {
"enabled": true,
"minVulnerabilityScore": 1.5,
"maxVulnerabilityScore": 10
}
} |
...
Yes
...
| Code Block |
|---|
"workflowRules": {
"enabled": true
} |
...
workflowRules.enabled
...
Boolean
...
Enables Workflow Rules being set from a .whitesource file.
Note: workflow rules can also be set in the Mend application in the Admin → Integration Workflow Rules. But if this parameter is set to true then Workflow Rules from the application are not being used.
...
Yes
...
true
...
workflowRules.minVulnerabilitySeverity
...
String
...
The minimal vulnerability severity level to automatically create remediation pull requests for. Allowed values - "LOW", "MEDIUM", "HIGH".
E.g. if set to "MEDIUM" then remediation pull requests of vulnerabilities with low severity will not be created - only for those with medium and high severity.
Note: if this parameter is used together with minVulnerabilityScore and maxVulnerabilityScore than only minVulnerabilitySeverity will have affect.
...
No
...
LOW
...
workflowRules.minVulnerabilityScore
...
Float
...
The minimal vulnerability CVSS 3 score to automatically create remediation pull requests for. Allowed values - floats with one decimal from 0 to 10.
For more information on CVSS 3 Scores, click here.
Note: if this parameter is used together with minVulnerabilitySeverity it will not have any effect.
...
No
...
Empty
...
workflowRules.maxVulnerabilityScore
...
Float
...
The maximal vulnerability CVSS 3 score to automatically create remediation pull requests for. Allowed values - floats with one decimal from 0 to 10.
For more information on CVSS 3 Scores, click here.
Note: if this parameter is used together with minVulnerabilitySeverity it will not have any effect.
...
No
...
Empty
Private Registry Settings (hostRules)
...
Parameter
...
Type
...
Description
...
Required
...
Default
...
matchHost
...
String
...
Defines where the credentials will be applied during the scan.
If you want to apply credentials only for a nested path within a host, then write matchHost as a base URL.
For example: https://registry.company.com/nested/path/.
If the same credentials apply to all paths on a host and not on any subdomains, configure matchHost with a protocol like https://registry.company.com.
Finally, to apply credentials to all hosts within the domain, use a matchHost value with no https:// prefix, e.g. company.com or registry.company.com, both of which would apply to a host like beta.registry.company.com.
...
No
...
Empty
...
hostType
...
String
...
Type of private registry. Supported values: npm (for both NPM and Yarn projects), maven, gradle, pypi, go , nuget, ruby.
Required if matchHost is used.
...
No
...
Empty
...
username
...
String
...
Used when credentials consist of username and password.
...
No
...
Empty
...
password
...
String
...
Used when credentials consist of username and password, should be encrypted by this instruction.
Encrypted secret that will be applied as a credential to the host set in the matchHost parameter. Must be included inside the encrypted parameter:
| Code Block |
|---|
"encrypted": {
"password": "3f832f2983yf89hsd98ahadsjfasdfjaslf............"
} |
...
No
...
Empty
...
token
...
String
...
Used when credentials consist of username and password, should be encrypted by this instruction.
Encrypted secret that will be applied as a credential to the host set in the matchHost parameter. Must be included inside the encrypted parameter:
| Code Block |
|---|
"encrypted": {
"token": "3f832f2983yf89hsd98ahadsjfasdfjaslf............"
} |
...
No
...
Empty
Providing a Global Configuration File
NOTE: Supported from version 20.5.1.3 only.
You can provide a custom .whitesource configuration file as part of the wss-bb-app container, in order to apply it globally to all of your organization's repositories. Doing so will apply the file to all onboarding pull requests for newly-selected repos. Repos which were already selected and activated before this change will not be affected by this global configuration. Only newly onboarded repos will be affected.
To apply this global change, do as follows:
Stop the wss-bb-app container.
In the "wss-bb-app/conf" folder, add your custom “.whitesource” file (where the prop.json file is located).
Start the wss-bb-app container.
Configuration Error Issues
Alert the user on configuration errors that affect their scan, by creating a configuration error issue and build status. In case of such an error, do as follows:
Stop the workflow. Do not create a scan or the Mend Security build status.
Create a “Configuration Failed” build status.
For each config file that failed parsing, create a new type of issue, entitled Action Required: Fix Mend Configuration File - {fileName}. If the error originated from the repo-config.json or global-config.json files, then the issue will be created in the whitesource-config repo.
Handled errors:
Error parsing the configuration files (.whitesource/repo-config.json/global-config.json json)
Missing repository and/or branch in the inheritance configuration
Upgrading to the Latest Docker Images
...
Get the latest Mend for Bitbucket Server version from Mend Support.
...
Upload the new Mend Bitbucket add-on by following the guidelines here.
...
Build these three Docker images from the new version - see here.
wss-bb-app
wss-scanner
remediate-server
Stop currently-running Docker containers from the previous version:
| Code Block |
|---|
docker stop <wss-bb-app> <wss-scanner> <remediate-server> |
Remove the Docker containers from the previous version:
| Code Block |
|---|
docker rm <wss-bb-app> <wss-scanner> <remediate-server> |
...
Fetch the activation key from the existing prop.json file (the propertyValue associated to the property "bolt.op.activation.key") and copy it to the clipboard.
...
Generate and save the new prop.json file by following the steps here and using the activation key value that was just copied.
...
Run the containers - see here.
...
(Optional) If the new wss-bb-app container has a different URL than the previous container, then follow the guidelines here to update the Bitbucket webhook URL.
Triggering a New Scan in Bitbucket
A scan is initiated via a valid 'push' command. A valid 'push' command meets at least one of the following requirements:
One of the commits in the 'push' command include added file(s) that have an extension supported by Mend and/or one of the commits in the 'push' command included a removal of file(s) that have an extension supported by Mend. Refer to the Mend Languages page in order to find out whether or not a specific language and its extensions are supported.
One of the commits in the 'push' command includes a modification in the package manager configuration file(s). This includes any of the following files as specified here.
Each time a valid 'push' command is made for a repository, Mend initiates a scan.
NOTE: The 'push' command may include multiple commits.
Handling Private Registries and Authenticated Repositories
| Info |
|---|
Private registries hosted on any platform that can be accessed with credentials are supported (Nexus, Artifactory, JFrog, etc.) |
Supported languages and package managers:
NPM
Yarn
Maven
Gradle
PIP
Go
Nuget
Ruby
In order to scan dependencies from private registries and authenticated repositories, Mend must be provided with credentials, such as an NPM token. These credentials must be added as encrypted secrets to the .whitesource file, either per-repository or in the shared global config, if the secret scope is org-wide.
Сreate the encrypted secrets. Each secret you encrypt must be scoped to a Bitbucket group or repository and use of it will be restricted to those within the app.
Use GPG to generate a PGP Key. Use the command
gpg --full-generate-keyand follow the prompts to generate a key. Please note that at this time we do not support using a passphrase for decryption, so it is best to generate the keys without a passphrase. Name and email are not important.Copy the key ID from the output or run
gpg --list-secret-keysif you forgot to take a copy. This is your public key.Run
gpg --armor --export-secret-keys YOUR_NEW_KEY_ID > ws-private-key.ascto generate an armored (text-based) private key fileRun
gpg --armor --export YOUR_NEW_KEY_ID > ws-public-key.ascto generate an armored (text-based) public key file
Provide the private key to the Controller, Remediate, and Scanner with environmental variable (learn more about environmental variables in the Advanced Technical Information documentation). There are two options for how to do it, but only one option should be used.
WS_HOST_RULES_PRIVATE_KEY- the value of the private key itself.WS_HOST_RULES_PRIVATE_KEY_FILE_PATH- path to the file containing the private key. This file should be mapped to the running containers.
Open index-enterprise.html in your favorite editor.
Find and replace the text "COPY_YOUR_PUBLIC_PGP_KEY_HERE" with your newly generated public key and save the file.
const publicKeyString = `COPY_YOUR_PUBLIC_PGP_KEY_HERE`;Generate a secret. There are the following fields on the encryption page:
Organization\Group - required, your Bitbucket group to which tokens secret be scoped.
Repository - optional, your Bitbucket repository to which secret should be scoped.
Raw value - required, confidential values/secrets such as tokens or passwords.
Encrypted value - the result of the encryption to be used in the integration.
After the secret is created, please add it to the hostRules parameter of the .whitesource file.
| View file | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Example of hostRules:
| Code Block |
|---|
{
"hostRules": [
{
"matchHost": "registry.npmjs.org",
"hostType": "npm",
"encrypted": {
"token": "3f832f2983yf89hsd98ahadsjfasdfjaslf............"
}
},
{
"matchHost": "https://custom.registry.company.com/maven/",
"hostType": "maven",
"username": "bot1",
"encrypted": {
"password": "p278djfdsi9832jnfdshufwji2r389fdskj........."
}
}
]
}
|
NOTE:
Copy the entire output of the key generator including comments to paste into the string.
i.e. include "-----BEGIN PGP PUBLIC KEY BLOCK-----..."
The string uses javascript backticks and not quotes. This is to allow a multi-line string so that you do not have to replace any line breaks with new-line characters. Be aware of any auto indenting by your editor that may introduce spaces to the public key and cause encryption to fail.
We use asymmetric public-key cryptography of the PGP methodology. Organization/Group, Repository, Raw Value - all information you provide on the encryption page is secured with this approach.
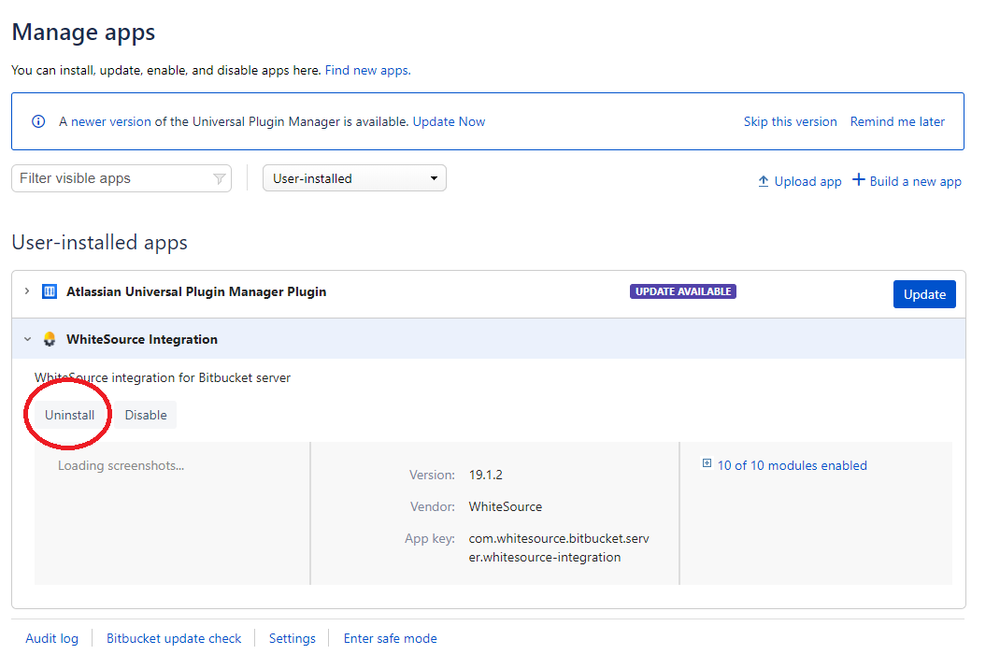
Uninstalling
You can easily uninstall this add-on by doing the following:
...
Select the Mend Integration app, and click on the ‘Uninstall’ button.
This page is available at: https://docs.mend.io/bundle/integrations/page/mend_for_bitbucket_server_and_data_center.html